Last updated: 08.01.2024
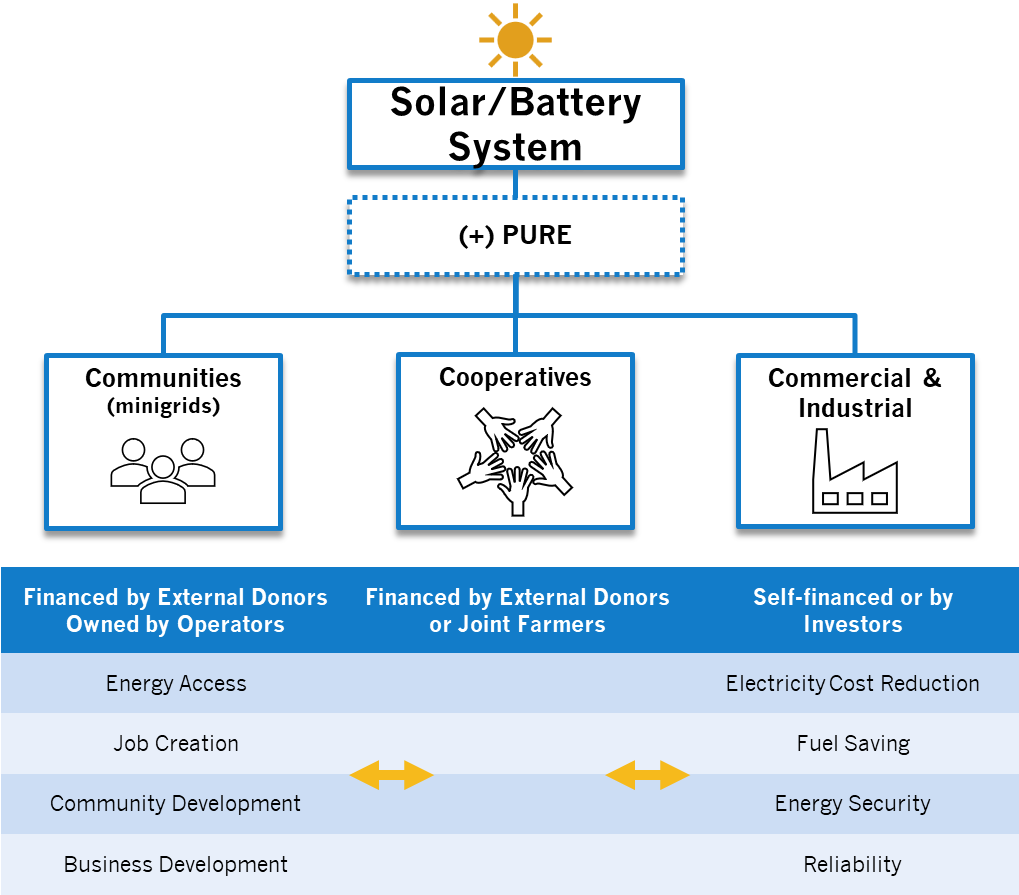
In rural communities in Africa, where grid infrastructure is often lacking or unreliable, access to electricity remains a major challenge. The development of solar minigrids has emerged as a viable solution in order to address this issue by distributing energy to remote villages in a decentralized and reliable manner. There are, however, many of these minigrids that only provide lighting and basic appliances to households, and as a result their impact on economic and social development is limited. Minigrids can be made more stable and robust through the use of digital tools and intelligent control systems. With digitalization, real-time monitoring becomes possible, facilitating proactive identification and resolution of technical issues, and intelligent control facilitates the management of load conditions. It will be further enhanced by the introduction of Productive Use of Renewable Energy (PURE) applications within the water-energy-food nexus.
Productive Use of Renewable Energy is an intriguing possibility which provides a wide variety of uses that could serve as a new frontier in livelihood and income-enhancing prospects for off-grid communities. Typical productive uses of rural areas in developing countries comprise restaurants (for lighting, refrigerators, mixers, cookers, etc…), agriculture and agro-processing activities (such as cold storage, milling, drying, packaging, etc…), water activities (such as pumping, purification, etc…) and manufacturing industries (such as carpentry, welding, wood processing, etc…). Aside from increasing rural productivity and economic growth, PURE also leads to a significant increase in rural employment, thus limiting urban migration and allowing the local community to expand beyond its traditional interests. A minigrid has the potential to attract more customers, increase power consumption, and thus increase profits by maximizing the usage of renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on batteries.
In every community, the bonds of unity are woven by the spirit of collaboration among its members. There has been a long tradition of cooperatives playing an important role in this synergy, uniting individuals in pursuit of shared needs and goals. Cooperatives ranging from agriculture to consumer services share a commitment to community well-being and equal opportunity. Yet, as communities evolve, so do the challenges they face. The absence of reliable grid infrastructure remains a significant hurdle in some parts of the world, such as rural Africa.
Cooperative Approach
A business model, based on the cooperative idea, involves a group of people who work together voluntarily to achieve economic, social, or cultural goals. Since a single member’s financial capacity is sometimes insufficient to cover the costs of equipment, devices, and other necessities alone, this model generally involves all members to share the financing. It also exemplifies the principles of collective ownership, democratic decision-making, community-centric operations, promoting cohesion, and facilitating access to financial support. By implementing this strategy, the cooperative has strengthened its financial health, enhanced its credibility, and increased its growth prospects. It allows to build a strong market presence, attracting additional customers and partners.
Combined with renewable energy solutions, the cooperative model emerges as a powerful catalyst for positive change for both agricultural and community service organizations. It embodies a powerful strategy for advancing sustainable and environmentally responsible energy solutions, which benefits its members as well as the surrounding community. This will allow them to achieve energy independence, cost reductions, and an uninterrupted supply of power for critical agricultural processes. In this collaborative framework, a group of people invest jointly in innovative solutions.
Incorporating a PURE hub into an agricultural cooperative operation enhances efficiency and effectiveness while contributing to broader goals such as community development, economic empowerment, and sustainable resource management. A cooperative of farmers could utilize renewable energy to power a cold storage facility. As a result, their produce remains fresher longer, minimizing post-harvest losses, and their market reach and profitability are increased. The same can be applied to a cooperative water treatment system that utilizes renewable energy to provide sustainable access to clean water. This addresses a fundamental community need, promotes public health, and establishes a business model that is economically viable through its ownership and facilities management.
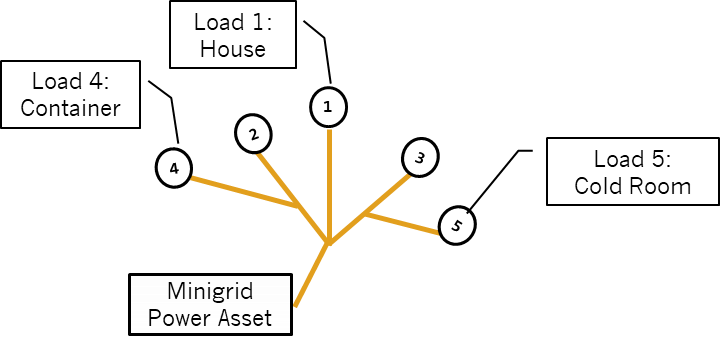
Minigrid Community / Cooperative Model
Now, consider the transition from running a collective business to commercial and industrial (C&I) sectors. Businesses and enterprises in this sector encompass a diverse range of activities, from manufacturing and warehousing to services and retail. Here, there are substantial energy demands as a result of the requirements for lighting, machinery, heating, cooling, and a variety of industrial processes. Energy reliability challenges can be encountered by C&I facilities, due to fluctuations in diesel prices and particularly in areas with unreliable or inadequate grid infrastructure.
Including solar power in off-grid businesses that rely heavily on diesel generators represents an important step in achieving higher energy reliability and greater fuel efficiency. With the use of battery energy storage systems, these businesses are able to eliminate their dependence on diesel generators or reduce the risk of grid outages. As a result, they are able to maintain an uninterrupted power supply, protecting themselves from the erratic nature of fuel prices. Similarly, businesses connected to the grid can enhance their energy security by leveraging solar energy. During times of grid outages, solar and battery systems serve as a reliable backup, ensuring uninterrupted operations. Aside from that, when grid electricity prices are high, solar power can provide an advantageous method of reducing the electricity costs.
C&I entities can benefit from the integration of solar energy as well as a PURE hub using intelligent control systems for dynamic load management. Their operations are optimized by strategically scheduling high-energy tasks during peak solar hours or at times when solar energy is abundant, thereby reducing operating costs and improving resource utilization. They are able to enhance sustainability, reduce their reliance on non-renewable resources, and reduce their carbon footprint. Increasing productivity and reducing waste will generate additional revenue streams, stimulate economic growth, and support local development.
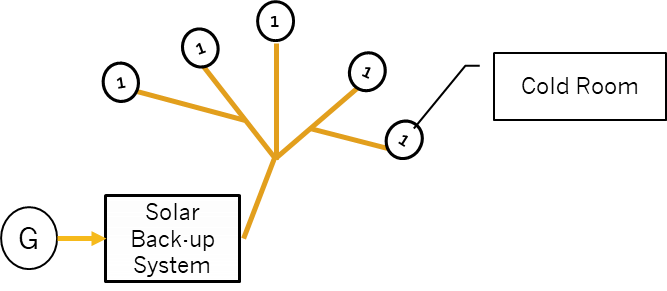
C&I Model
In summary, the primary objective of this PURE hub approach is to demonstrate the benefits of integrating solar powered productive use applications in rural electrification, cooperative models, and Commercial & Industrial (C&I) businesses. In particular, it aims to achieve the following sub-objectives:
- Increase access to reliable and sustainable energy for productive use in rural communities.
- Strengthening cooperative business models via PURE initiatives to enhance economic viability collectively.
- Improve energy resilience and reduce cost reduction for C&I facilities through the integration of renewable energies into their everyday businesses.
- Enhance operational processes through the intelligent integration of PURE applications.
- Improve the socio-economic development of rural communities through the creation of income-generating activities.
If you are interested in learning more about what we do, or inquiring for a project with us, do not hesitate to contact us at: pure@asantys.com.
You can also access and download our different solutions datasheets here:
 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch
